As teacher candidates, we are acquiring knowledge and skills to understand and begin to apply the Teacher Performance Expectations. We utilize the TPE’s because they also align with how districts will assess us and our readiness when we apply for a teaching position. After we receive our first teaching assignment, we will be required to clear our credentials. Guess what, the TPE’s come into play again! Induction programs (for clearing our credentials) will evaluate our strengths and growth areas as new teachers. In this course and future courses, the TPE assignments will get us prepared and thus help us begin our own individual growth plan as we become a teacher. The goal is to be able to articulate and talk about our teaching practice using the academic language found in the TPEs, and our coursework will support this mission!
Download
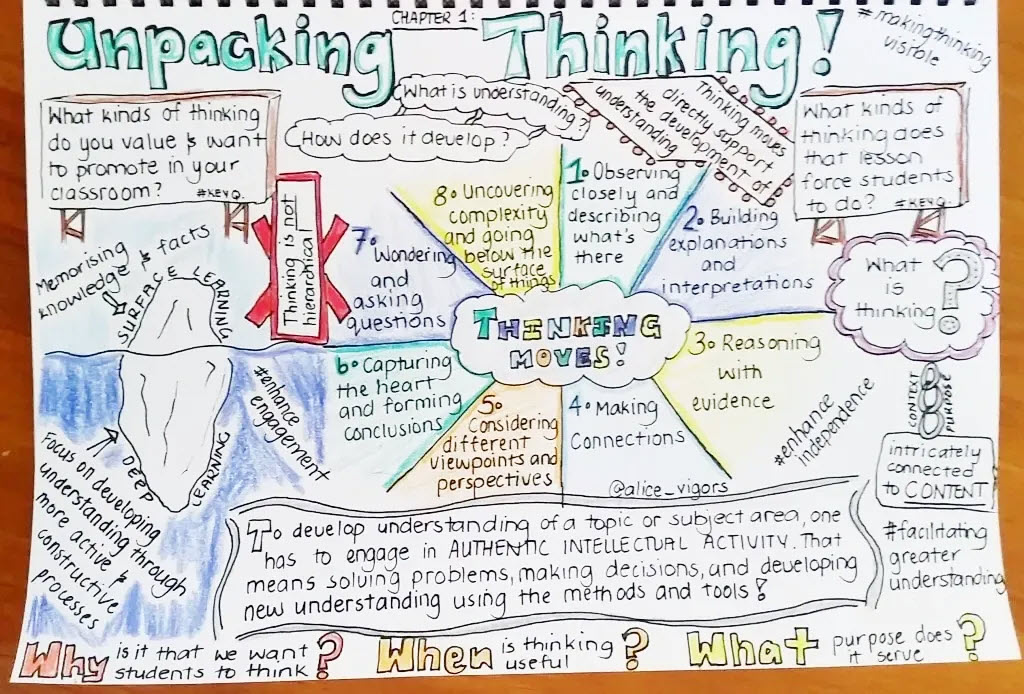
TPE Evidence for Observations PDF CTC TPE Handbook of Multiple and Single Subject Credential Program Standards Understanding how to Unpack Standards
Considerations
As we internally reflect on our assets/strengths and areas of growth, remember we are considering ALL students, not just the students whom we easily connect with but also the students who we may need to learn more about to engage them (cognitively and/or emotionally). It is natural that we build relationships with those whom we have experiences or backgrounds that are similar; it is sometimes more difficult to engage with others whom we have differences with (religion, socioeconomic, gender, ethnicity, race).
Differentiation
Throughout this program we will differentiate for Interns & Student Teachers in various assignments and activities. We will also differentiate for multiple and single subject credential programs. The goal is to connect your own lived experiences, knowledge, and your credential area to all aspects of your learning. If you feel an assignment or activity does not differentiate please share this with the Course Lead so adjustments can be made.
Intern Teacher
As Intern Teachers, we will complete this reflective practice activity of the Teacher Performance Expectations taking into consideration our current classroom of students. If we do not have a classroom yet, we were to view this assignment through the lens of a student teacher.
Student Teacher
As Student Teachers who do not currently have a classroom, we were to reflect using our personal assets/strength areas (what comes naturally to us, and draw from past experiences) and what areas we will need to engage in professional activities for growth.
TPE 1.1
Apply knowledge of students, including their: prior experiences, interests, and social-emotional learning needs, as well as their funds of knowledge and cultural, language, and socioeconomic backgrounds, to engage them in learning.
Directions: Self-evaluate by highlighting the elements of the TPE in:
Italic if you are not familiar with the TPE
Underline if you are moderately confident with the TPE
Bold if you are very confident with the TPE
Student teacher: Consider your ability to engage others based on your knowledge of what you know about them. From the examples of evidence, select which ones you feel come natural to you.
Intern: Consider your ability to engage and support ALL your students. Reflect on your relationships with your students and select from the examples of evidence which ones you feel are your assets/strengths.
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.1 – Current Assets and Strengths
- Provides vehicles so that students begin taking ownership of their learning; track own progress, journals, writing activities prior/after
- Provides opportunities for students to use available technologies, ensuring equitable access to the curriculum
- Differentiates instruction based on students’ strengths, interests, and needs
- Builds trust with and among students and fosters relationships so that students can thrive academically
- Helps students build friendships with each other
- Fosters relationships and develops activities so that students can thrive academically
- Shows respect for students and encourages them to show respect to others
- Understands reasons for students’ behavior and recognize atypical student behavior
- Develops activities that support positive interactions among students
- Provides opportunities for students to work together
- Creates and maintains a safe learning environment
- Adapts teaching to reflect comprehensive knowledge of students
- Gets to know parents and connect with the teaching community.
Identify 3 Areas of Growth and an Action you will take Directions: Identify 3 areas of growth with an action you will take to improve this area.
Ownership of Learning:
Action: Create a structure that encourages students to track their own progress, keep learning journals, and write reflectively before and after lessons. Providing students with a learning portfolio or digital tools to track their progress and take control of their learning could help..
Equitable Access to Technology:
Action: Provide opportunities for all students to use technology in the classroom so they have equal access to it. Technology-rich activities can be incorporated into the curriculum, access to devices or computer labs can be provided, and partnerships can be explored with organizations that support digital inclusion.
Differentiated Instruction:
Action: Provide students with a variety of instructional strategies and resources that suit their strengths, interests, and needs. This could mean identifying individual learning styles, offering flexible learning pathways, and providing enrichment or support activities tailored to each student.
TPE 1.2
Maintain ongoing communication with students and families, including the use of technology to communicate with and support students and families and to communicate achievement expectations and student progress.
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.2
Examples of Observable Evidence: How do you maintain ongoing communication with students to communicate achievement expectations and progress?
Examples may include:
- Agendas
- Remind
- Jupiter grades
- Phone Logs
- Classroom Dojo
- Power School
- Text
- Other
How do you maintain ongoing communication with parents to communicate achievement expectations and progress?
- Blackboard
- Jupiter grades
- Classroom Dojo
- Weekly letter, newsletter
- Progress reports, grades
- Parent conferences: student-led
- Family night
- Other
Additional Resources:
Best Messaging Apps and Websites for Students, Teachers, and Parents
How Two-Way Communication Can Boost Parent Involvement
(https://www.waterford.org/education/two-way-communication-parent-engagement/)
Current Assets And Strengths
Student Teacher and Intern Teacher: Consider your ability to communicate in an effort to build relationships, share expectations, and progress.
Describe: What methods of communication do you currently have strengths in?
I mostly communicate by email and text. I also know how to assign grades and report progress.
Growth
Describe the communication tools you need to investigate and practice using?
Jupiter Grades: With Jupiter Grades, teachers, students, and parents can communicate easier. Mostly it’s for tracking grades, assignments, and academic progress.
Classroom Dojo: Classroom Dojo is a communication and behavior management tool that helps teachers, students, and parents communicate in real-time. Using it, teachers can track student behavior, share updates, and give feedback.
PowerSchool: Schools use PowerSchool to manage student data, including attendance, grades, schedules, and more. Additionally, it offers tools for students, teachers, and parents to communicate.
TPE 1.3
Connect subject matter to real-life contexts and provide active learning experiences to engage student interest, support student motivation, and allow students to extend their learning.
Directions: Self-evaluate by highlighting the elements of the TPE in:
Italic if you are not familiar with the TPE
Underline if you are moderately confident with the TPE
Bold if you are very confident with the TPE
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.3 – Current Assets and Strengths
Examples of Observable Evidence:
- Establishes a connection between subject matter and purpose for learning: videos, posters, illustrations, realia, etc.
- Provides ongoing feedback regarding the relevance/connection of subject matter to their lives
- Engages students in multi-modality instructional strategies
- Differentiates instruction based on students’ strengths, interests, and needs
- Instructional strategies: surveys, exit tickets, jigsaw, skill inventories, interest centers (review/enrich), literature circles, collaborative grouping, peer mentoring/modeling, Socratic seminars, etc.
Identify 3 Areas of Growth and an Action you will take Directions: Identify 3 areas of growth with an action you will take to improve this area.
- Establishing the Connection Between Subject Matter and Purpose for Learning:
- Action: Include visual aids, such as videos, posters, illustrations, or real-life examples, to demonstrate the relevance and purpose of the topic. Students can connect the content to their lives and the world around them through class discussions.
- Providing Ongoing Feedback on Relevance and Connection of Subject Matter:
- Action: To gauge their understanding, ask students for feedback regularly through surveys, discussions, or exit tickets. Change instruction approaches based on their feedback and provide examples or explanations that make the content more relatable.
- Differentiating Instruction Based on Students’ Strengths, Interests, and Needs:
- Action: Assess student strengths, interests, and learning needs with surveys, tests, or skill inventories. This information can be used to tailor instruction by offering choice-based activities, grouping students based on their preferences, providing extension opportunities for advanced learners, and offering targeted support to students who need more help.
TPE 1.4
Use a variety of developmentally and ability-appropriate instructional strategies, resources, and assistive technology, including principles of Universal Design of Learning (UDL) and Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) to support access to the curriculum for a wide range of learners within the general education classroom and environment.
Directions: Self-evaluate by highlighting the elements of the TPE in:
Italic if you are not familiar with the TPE
Underline if you are moderately confident with the TPE
Bold if you are very confident with the TPE
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.4 – Current Assets and Strengths
Examples of Observable Evidence
- Universal Design for Learning Engagement:
- Class discussion: verbal response; pair share; peer mentoring/teaching/presentation
- Differentiation
- Present information in different ways: verbally, written on board, overhead, videos
- Process: 1:1 instruction, small or large group; pair share; use proximity; use SDAIE strategies
Resources: Definition of Multi-Tiered System of Supports
Identify 3 Areas of Growth and an Action you will take
Directions: Identify 3 areas of growth with an action you will take to improve this area.
- Universal Design for Learning Engagement:
- Action: Implement Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles to make learning more engaging. The process includes multiple ways to represent, act and express, and engage. Provide students with diverse instructional materials and formats, give them autonomy, and incorporate interactive and hands-on learning activities that cater to their learning styles.
- Differentiation:
- Action: Differentiate instruction based on student needs. Take individual learning styles, interests, and readiness levels into account. Using flexible grouping strategies, offering choice-based assignments or projects, providing additional support or enrichment activities, and assessing student progress regularly will help differentiate lessons.
- Process: 1:1 Instruction, Small or Large Group, Pair Share, Proximity, SDAIE Strategies:
- Action: Take a look at the different instructional approaches and strategies that can help students learn. To provide personalized support, give 1:1 instruction or small group activities, encourage pair sharing to promote peer learning, and use proximity to offer individual attention and support. Use Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English (SDAIE) strategies to scaffold content for English language learners.
TPE 1.5
Promote students’ critical and creative thinking and analysis through activities that provide opportunities for inquiry, problem-solving, responding to and framing meaningful questions, and reflection.
Directions: Self-evaluate by highlighting the elements of the TPE in:
Italic if you are not familiar with the TPE
Underline if you are moderately confident with the TPE
Bold if you are very confident with the TPE
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.5 – Current Assets and Strengths
Examples of Observable Evidence
- Instructional strategies: Corners, hot seat, role play, analyze characters – ask character questions
- Demonstrate comprehension via projects/visual medium: paintings, poems
- Math: What is the result; what type of function; is this predictive of functions…
- Reading A Musical Day…short /o/ sounds; think about words; sounded out; rapid fire; whole group; kinesthetic activities; critical thinking-questions, personal experiences…
Identify 3 Areas of Growth and an Action you will take
Directions: Identify 3 areas of growth with an action you will take to improve this area.
- Instructional Strategies: Corners, Hot Seat, Role Play, Analyze Characters – Ask Character Questions:
- Action: Enhance student engagement and comprehension by exploring and incorporating more instructional strategies. Consider other approaches like think-pair-share, interactive simulations, debates, and hands-on experiments. Use strategies that promote active participation and a deeper understanding of the lesson objectives.
- Math: Result, Type of Function, Predictive of Functions:
- Action: Enhance students’ understanding of math concepts by using a variety of strategies. Engage students in problem-solving activities that require them to identify the results, figure out the type of function, and explore how functions work. Make math concepts more relatable and tangible with real-life examples, hands-on manipulatives, and interactive technology.
- Reading “A Musical Day” – Short /o/ Sounds, Word Analysis, Rapid Fire, Critical Thinking:
- Action: Engage kids in phonics and reading comprehension activities. Create lessons that focus on sounds and word analysis, like identifying and categorizing words with the targeted sound. Through open-ended questions and discussions, use rapid-fire reading exercises to improve fluency and critical thinking. Use kinesthetic activities, like movement or gestures, to engage students and reinforce their understanding.
TPE 1.6
Provide a supportive learning environment for students’ first and/or second language acquisition by using research-based instructional approaches, including focused English Language Development, Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English (SDAIE), scaffolding across content areas, and structured English immersion.
Demonstrate an understanding of the difference among students whose only instructional need is to acquire Standard English proficiency, students who may have an identified disability affecting their ability to acquire Standard English proficiency, and students who may have both a need to acquire Standard English proficiency and an identified disability.
Directions: Self-evaluate by highlighting the elements of the TPE in:
Italic if you are not familiar with the TPE
Underline if you are moderately confident with the TPE
Bold if you are very confident with the TPE
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.6 – Current Assets and Strengths
Examples of Observable Evidence
- Uses a wide variety of instructional strategies matched to students’ learning needs that offer several ways for students to approach and demonstrate learning
- Facilitates students’ use of available technologies to support and/or advance their learning
- Offers opportunities for students to explore important ideas using a variety of resources and available technologies
- Offers students choice within teacher and state frameworks
- Taps prior knowledge and links it to new learning
- Provides support for students who are not succeeding
- Provides opportunities for advanced learners to enhance their learning
- Reflects on the learning goals/objectives
- Reflects on students’ developmental needs
- Plans and implements lessons that reflect students’ individual strengths and cultural norms
- Encourages participation in a variety of ways
- Allows time for students to practice, internalize, and apply subject-specific learning strategies
- Plans and implements activities and materials that are developmentally appropriate to ensure all students understand essential learning goals
- Makes modifications for students who have specific physical, emotional, behavioral, language, or learning differences
- Uses resources that minimize bias
- Facilitates group activities that maximize productivity and increase engagements
Identify 3 Areas of Growth and an Action you will take
Directions: Identify 3 areas of growth with an action you will take to improve this area.
- Uses a Wide Variety of Instructional Strategies Matched to Students’ Learning Needs:
- Action: Adapt instructional strategies to cater to different learning styles. Inquiry-based approaches, hands-on activities, multimedia presentations, and individualized instruction are some strategies that can be used. Adapt instruction strategies based on student progress to ensure effective learning.
- Offers Opportunities for Students to Explore Important Ideas Using a Variety of Resources and Available Technologies:
- Action: Use traditional and digital resources to explore and engage with important concepts. Make it easy to access books, articles, videos, online databases, etc. Analyze and synthesize multiple sources of information to help students understand the subject.
- Uses Resources That Minimize Bias:
- Action: Select and use instructional resources that minimize bias and promote inclusivity. Check textbooks, reading materials, videos, and online resources for accurate representations of diverse perspectives, cultures, and identities. Seek out diverse resources and perspectives to encourage understanding and empathy.
TPE 1.7
Provide students with opportunities to access the curriculum by incorporating the visual and performing arts as appropriate to the content and context of learning.
Directions: Self-evaluate by highlighting the elements of the TPE in:
Italic if you are not familiar with the TPE
Underline if you are moderately confident with the TPE
Bold if you are very confident with the TPE
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.7 – Current Assets and Strengths
Examples of Observable Evidence
- Incorporate art and music projects
- Project-based instruction with visual and performing arts strategies incorporated
Identify 3 Areas of Growth and an Action you will take
Directions: Identify 3 areas of growth with an action you will take to improve this area.
- Incorporate Art and Music Projects:
- Action: Enhance student engagement and foster creativity with art and music projects. Include activities like creating visual artworks related to a topic, composing music, exploring music genres, or designing multimedia presentations that mix music and art. This is a great way for students to show off their artistic talents and express their understanding of content.
- Project-Based Instruction with Visual and Performing Arts Strategies Incorporated:
- Action: Incorporate visual and performing arts strategies into project-based instruction to promote deeper learning. Design projects that let students explore topics or concepts through art, drama, dance, or music. Enhance understanding and provide hands-on experiences with visual representations, skits and plays, choreographies, and music compositions.
TPE 1.8
Monitor student learning and adjust instruction while teaching so that students continue to be actively engaged in learning.
Directions: Self-evaluate by highlighting the elements of the TPE in:
Italic if you are not familiar with the TPE
Underline if you are moderately confident with the TPE
Bold if you are very confident with the TPE
Examples of Evidence of TPE 1.8 – Current Assets and Strengths
Examples of Observable Evidence
- Encourages students to develop and have confidence in their own ability to think independently and with others
- Builds on basic knowledge and skills to enable students to apply their thinking to solving problems
- Breaks down text into component parts through an understanding of structure (topic, subtopic, claims, evidence, sequence, and comparison)
- Uses rubrics and guidelines to evaluate work in progress
- Develops anchor papers at high, high average, low average, and struggling levels of performance
- Builds plans to address and answer questions in accordance with Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Groups students in pairs or small working groups to develop a plan to solve problems presented by teachers
- Allows adequate time for students to think about their answers
- Provides opportunities to collect and interpret data
- Assigns activities that include more than one method of approaching or completing work
- Systematically checks for student understanding and revises plans accordingly
- Implements a variety of instructional strategies to match students’ learning needs
- Offers several ways for students to approach and demonstrate learning
- Paces lesson to adjust to student needs
- Provides additional support for students who have mastered lesson objectives
- Adjusts lessons “on the spot”
Identify 3 Areas of Growth and an Action you will take
Directions: Identify 3 areas of growth with an action you will take to improve this area.
- Breaks Down Text into Component Parts through Understanding of Structure (Topic, Subtopic, Claims and Evidence, Sequence and Comparison):
- Action: Teach students how to analyze and deconstruct texts based on their structure. Explain how to identify main topics, subtopics, claims, evidence, and sequences or comparisons within the text. Provide scaffolding to help students practice breaking down complex texts. Support comprehension and analysis of text structures with graphic organizers, visual aids, and guided questions.
- Assigns Activities That Include More Than One Method of Approaching or Completing Work:
- Action: Offer multiple ways to approach and complete assignments so students have a choice. Make it easy for students to demonstrate their understanding with different formats, mediums, or strategies. Provide resources, materials, and technology to support diverse learning styles. Give students more control over their learning by letting them take charge.
- Offers Several Ways for Students to Approach and Demonstrate Learning:
- Action: Give students multiple ways to approach and demonstrate their learning. Include different types of expression, like writing assignments, presentations, visuals, multimedia projects, or performances. Adapt assignments to students’ interests, learning styles, and abilities with choice boards, menus, or flexible assignments. Select approaches that align with students’ strengths and preferences so they take ownership of their learning.
Assignment Grade: 12/12